You have several choices in how to deploy Azure DevOps on-premises. You can install everything on a single server. Or, you can use multiple application tiers and SQL instances. For information about how to determine the right type of deployment for your team, see Hardware recommendations.
Azure DevOps Server supports the Analytics Service which can be used in place of SQL Server Reporting Services or along side it. However, if you plan to use the Inheritance process model to customize work tracking, you can only use the Analytics Service for reporting, the project collection must not be configured to support reporting.
To learn more about the Analytics Service, see What is the Analytics Service?. To learn more about the Inheritance process model, see About process customization and inherited processes.
Only new project collections can be configured to support the Inheritance process model. Upgraded project collections can only continue to support the On-premises XML process model.
If you set up Azure DevOps on-premises for personal use or to evaluate it, use Azure DevOps Express. Azure DevOps Express is free, simple to set up, and installs on both client and server operating systems. It supports all of the same features as Azure DevOps Server. Azure DevOps Server Express licensing limits use to five active users.
Consider using a free Azure DevOps Services organization for personal use. Because Azure DevOps Services are cloud-based, you don't need to install them on your own hardware or manage your own backups.
No matter how you plan to deploy Azure DevOps Server, the process involves the following three steps:
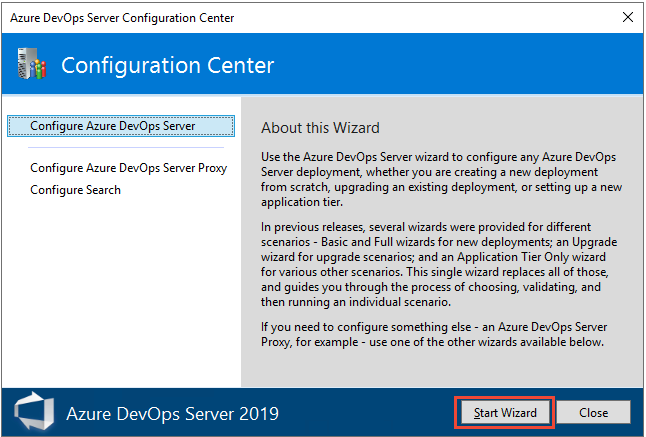
When installation finishes, the installer starts the Azure DevOps Server Configuration Center. A unified wizard supports all Azure DevOps Server configurations, such as new installations, upgrades, and application-tier-only scenarios.
Customizations made outside of the Configuration Center wizard may not be retained during upgrades. If you have implemented additional customizations, it is recommended to reapply them after the upgrade process. It is also advisable to refrain from modifying the web.config file. Furthermore, adding indexes, triggers, or fields to any of the databases is not supported and may result in an unsupported environment, potentially hindering future upgrades.

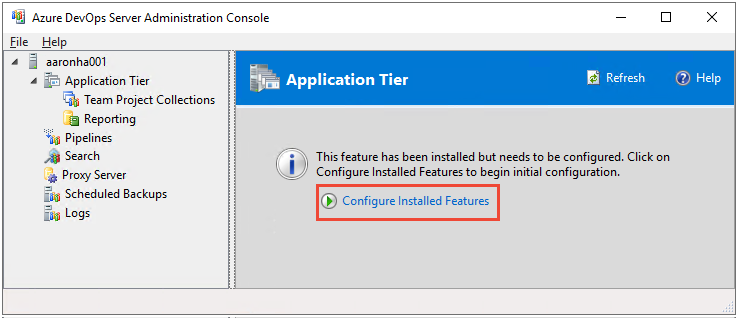
If you need to close the Configuration Center dialog, you can return to it. Start the Azure DevOps Server Administration Console, and select Configure Installed Features from the Application Tier, Search, or Proxy Server page. This option is only available when there are settings that still need configuration. For example, once the application tier has been fully configured, then you can only modify settings through the Azure DevOps Server Administration Console, Application Tier page.
The Server Configuration Wizard supports three main configuration options: Basic, Advanced, and Azure.
Choose Basic when you want to configure the application-tier server and install and configure the Search extension, or configure some other third party search feature. Installing and configuring Search supports Code, Work Item and Wiki search features. To learn more, see Configure search.
Choose Advanced when you want to configure your deployment to support SQL Server Analysis Services and SQL Server Reporting Services, in addition to the features configured with the Basic option.
Advanced is not available on Azure Virtual Machines. Use either Basic or Azure.
Choose Azure when you have installed Azure DevOps Server on an Azure Virtual Machine and want to configure it using Azure SQL Database. For details, see Use Azure SQL Database with Azure DevOps Server.